Unanimity
Decision Method
Unanimity means everyone has a vote. The decision depends on everyone’s full agreement with the decision.
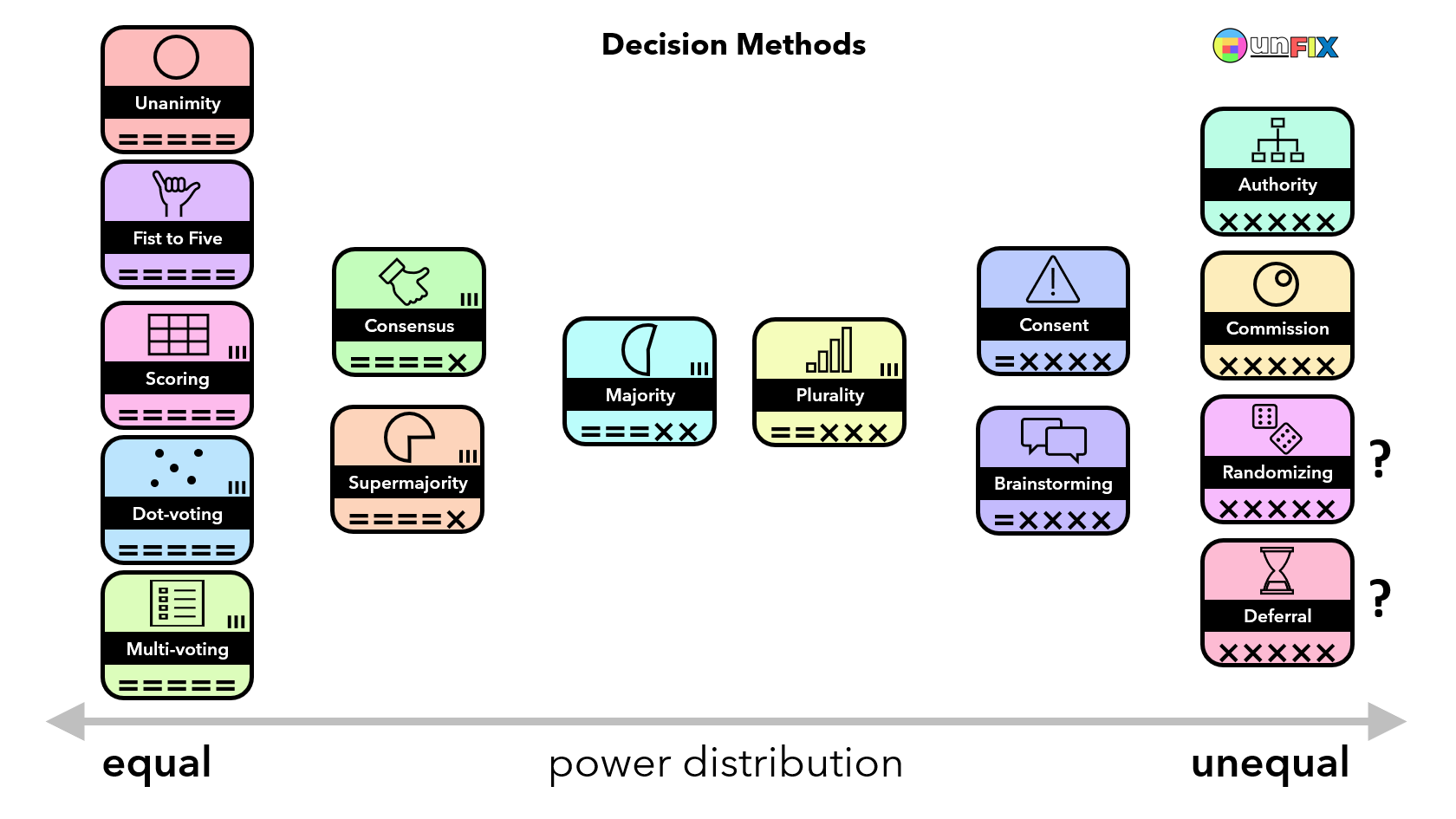
Decision Methods: Unanimity • Fist to Five • Scoring • Dot-Voting • Multi-Voting • Consensus • Supermajority • Majority • Plurality • Consent • Brainstorming • Authority • Commission • Randomizing • Deferral
Purpose
Unanimity is a decision-making method rooted in the belief that collective decisions should reflect the complete agreement of all participants involved. When a decision is said to be unanimous, it means that every individual in the group has cast their vote in favor of the proposed idea or action, without any dissent. This ensures that everyone's perspectives and concerns are acknowledged and addressed. Unlike majority rule, where a decision may proceed with even a slim margin of agreement, unanimity requires full and total alignment. It emphasizes harmony, shared understanding, and the collective will of the group, ensuring that decisions are truly representative of the entire community's desires and aspirations.
Unanimity differs from Consensus and Consent.
Unanimity = everyone says Yes or Hell, Yes.
Notes
Unanimous decision-making carries several benefits as well as drawbacks. On the positive side, unanimous decisions foster a sense of unity, trust, and cooperation among team members, promoting a harmonious and collaborative work environment. They also indicate a high level of consensus and shared commitment, leading to swift implementation and reduced conflicts. Additionally, unanimous decisions tend to result in higher levels of satisfaction and engagement among team members, as everyone feels heard and included. However, there are also drawbacks to unanimous decision-making. It can potentially stifle dissenting opinions and innovative thinking, leading to groupthink and a lack of critical evaluation of alternatives. Unanimous decisions may also slow down the decision-making process, as it requires reaching a consensus that satisfies all team members.
Rules / Constraints
We have not yet defined rules or constraints for this decision method.




“Sometimes you make the right decision, sometimes you make the decision right.”
(Source: Phil McGraw)