Supermajority
Decision Method
Supermajority means everyone has a vote. The decision is done on a significant majority being in favor of the decision.
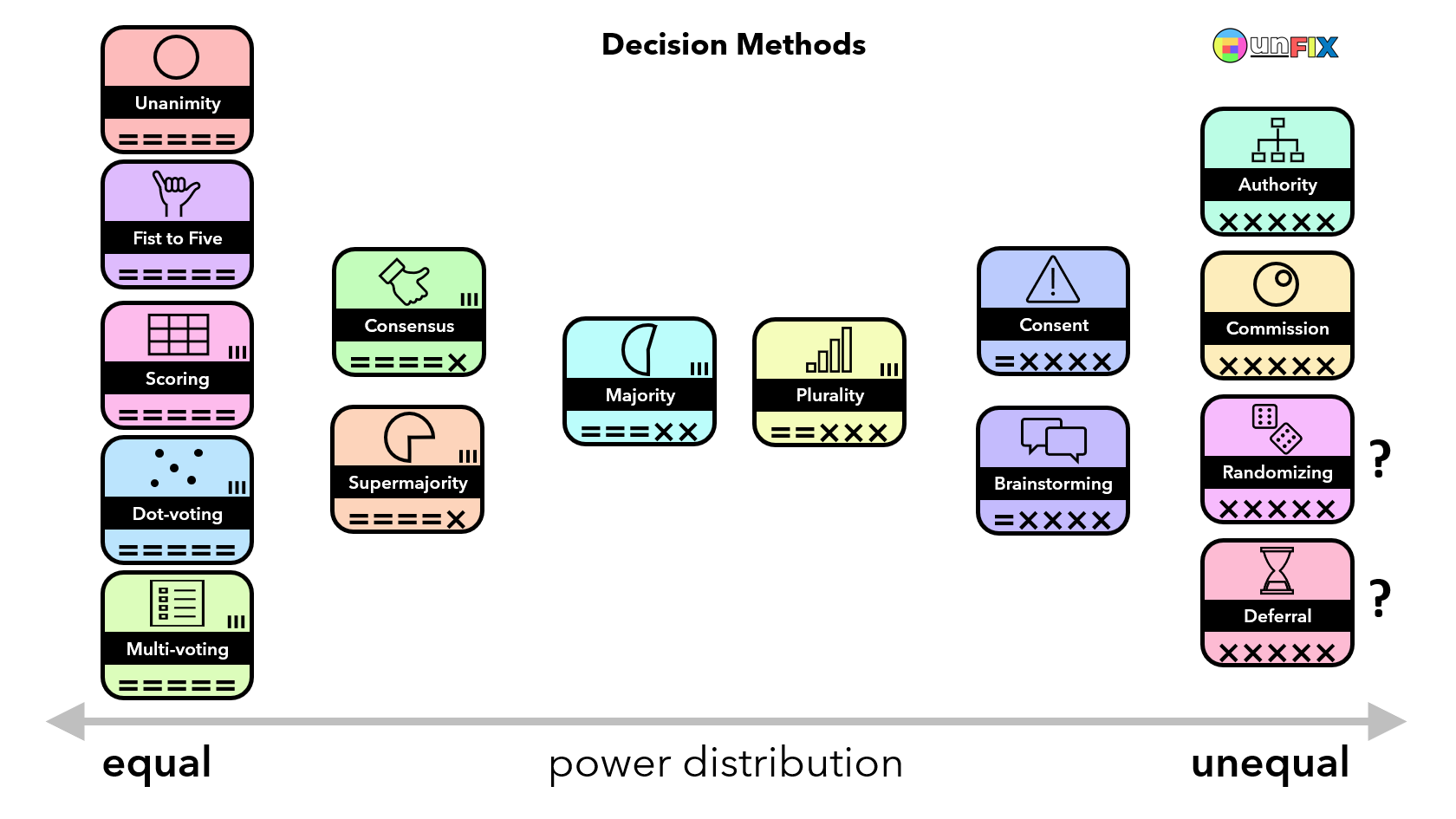
Decision Methods: Unanimity • Fist to Five • Scoring • Dot-Voting • Multi-Voting • Consensus • Supermajority • Majority • Plurality • Consent • Brainstorming • Authority • Commission • Randomizing • Deferral
Purpose
Supermajority is a decision-making method that goes beyond simple majority rule. While in many situations, a decision might proceed with just over half of the votes, a supermajority requires a much higher percentage of approval. Every participant has a voice and a vote, but for a decision to be ratified, it needs to secure support from a significant majority, often defined as two-thirds, three-quarters, or another stipulated threshold. This method ensures that decisions are not merely accepted by a slim margin but have substantial backing, reflecting a broader alignment. By adopting a supermajority standard, organizations or groups can make decisions that are more resistant to divisive issues and ensure a wider acceptance and commitment among their members.
Notes
Supermajority decision-making can contribute to increased deliberation, thorough discussion, and the exploration of alternative viewpoints, fostering a more cautious and thoughtful approach to important choices.
Rules / Constraints
We have not yet defined rules or constraints for this decision method.




“Sometimes you make the right decision, sometimes you make the decision right.”
(Source: Phil McGraw)